Written by
Meghna Elizabath Zachariah
M.Sc., B.Ed in Special Education
Special Education Department
All children have the right to grow and learn in an accepting and safe environment. Differently abled children are often admitted to special schools where they learn along with other differently abled children. What if these children are taught in regular schools? Would they benefit if they are accommodated in a regular school? Will they be able to cope with the challenges of regular schooling? How can children be accommodated in regular schools? Let us see!
Understanding Inclusion and Mainstream Classrooms :
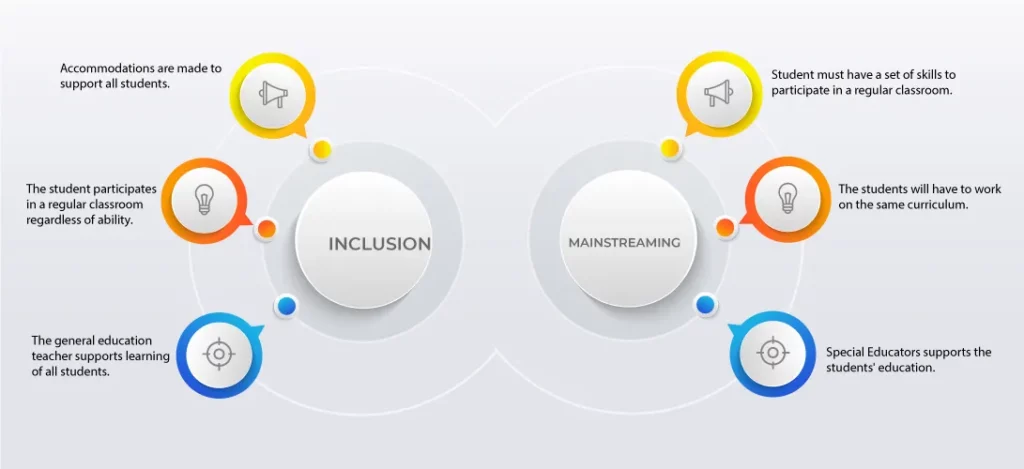
Both mainstreaming and inclusion involve including children in a regular classroom. However, there is a difference. Let’s see what it is!
In mainstreaming, students are expected to learn the same curriculum. However, adaptations are made to help them access learning. For example, if a class is expected to answer a question in a paragraph, a student with special needs may just have to write the key points. Accommodations are made to help them access learning and demonstrate their learning. Children may be taking individual sessions for learning support.
In inclusion, the child with special needs may not be expected to learn the same content as their peers. The main focus is on social skill development and access to education. The content may be reduced, or alternative goals may be taken. For example, a child with special needs may be expected to learn a more simple topic or easier content. Teachers present content in multiple ways to include all types of learners. Modifications are made in what is presented, the activities given and how learning is demonstrated.
Identifying and Assessing Students with Special Needs:
A child with special needs may show different signs and symptoms in a classroom. They may show behaviour issues, poor social interaction, and/or poor progress. Teachers in a classroom must note these signs and discuss them with the parents regarding assessment.
Recognizing Different Types of Disabilities:
After a thorough assessment by a qualified professional, a child’s difficulty can be understood. It helps to place a treatment specific to their need and abilities. It helps to understand what the child can achieve.
Assessing Student’s Strengths and Needs:
It is important to know the strengths of the child. The strengths of the child can be used to help the child develop other skills. An individualized education plan is prepared based on the needs of the child.
Individualized Education Plan (IEP):
An IEP is a plan that is developed based on an individual’s needs. It is prepared by a multidisciplinary team to ensure holistic development of the child. It lays out the different services and supports a child requires. It also states the goals the child should achieve within a specific period of time.
Creating an Inclusive Classroom Environment:
An inclusive classroom ensures that all children, irrespective of their needs, cultural background, or language, have equal access to learning. A child with special needs and also a gifted child must feel supported and challenged in an inclusive classroom.

Universal Design for Learning(UDL):
Universal design for Learning is an approach to developing a curriculum in such a way that all learners are accommodated. It states that content should be presented in multiple ways, plan variety of activities to help students learn, to provide multiple options to present what children know.
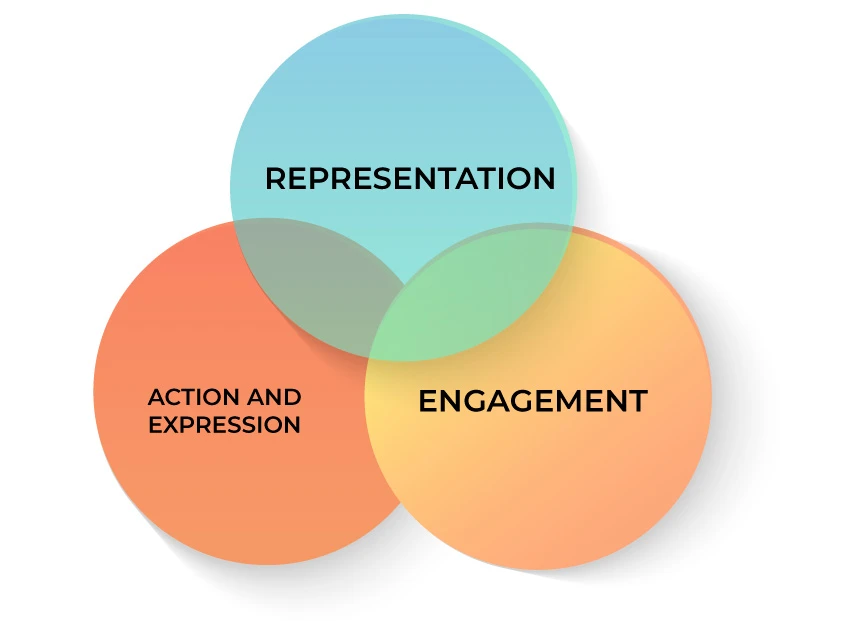
Multiple means of Representation:
This includes presenting information in a variety of ways so that all learners can access learning. Using hands-on activities, field trips, group activities, and role plays in a classroom can help students learn better.
Multiple means of Engagement:
This includes providing a variety of opportunities for students to participate. Providing activities and projects to learn and practice what is learnt can be useful.
Multiple means of Action and Expression:
This includes providing a variety of options for students to demonstrate learning. For example, instead of a written assignment, students can be asked to demonstrate their learning through a diorama or verbally.
Incorporating the principles of UDL can help teachers to apply different methods of teaching and assessments. This reduces barriers and provides equal opportunities for children to access learning and demonstrate their potential.
Accommodations and Modifications for Students with Special Needs:
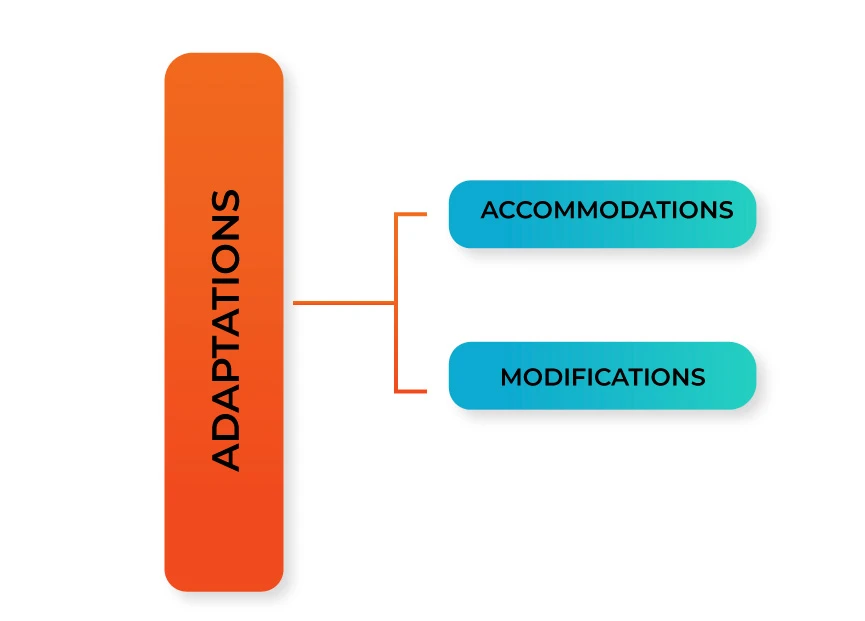
Adaptations are changes made in the learning environment to enable all learners to learn. Changes can be made in the way content is presented, in the way students engage in learning, in the way learning is demonstrated and also in the learning environment. Adaptations in the classroom are made in the form of accommodations and modifications.
Accommodations are those changes made that do not alter the goals. For example, changes can be made in the environment, and the amount of time to complete an activity can be increased. All these do not lower the expectation level of students.
Modifications include changing or lowering the expectation of students compared to their peers. For example, the difficulty level of a content can be reduced by reducing the amount of content a child is expected to learn.
The key to a successful inclusive classroom is to make necessary adaptations in the classroom so that no learner is excluded.
Collaboration in Inclusive Education
Collaboration is a necessary factor to ensure a supportive and positive learning environment for all. It plays a vital role in the development of the child. Collaboration between parents and teachers, Special educators and other professionals, school and community is important for the overall development of the child.
Parent-Teacher Collaboration
It is important for parents and teachers to communicate with each other. Parents know the child better and can communicate regarding the strengths of the child initially. It is important for teachers to state the level of expectation, the goals, the progress the child has made, and any challenges faced. Parents can also communicate whether the child has generalized the learnt skills. Parents can stand as advocates for their children.
Special Educator-Teacher Collaboration
Special Educators can guide regular teachers on how to make adaptations. Their goals, needs and teaching strategies can be discussed. Proper communication between teachers and special educators is extremely important for positive, inclusive practices.
School-Community Collaboration
Children are a part of all the activities in the community. It is important for students to be able to participate in the community. Communities can help in identifying children with needs, creating awareness and also in providing various services and activities. The transition from school to vocation can also be supported by the community. Schools must collaborate with different organizations to ensure the positive participation of students in the community
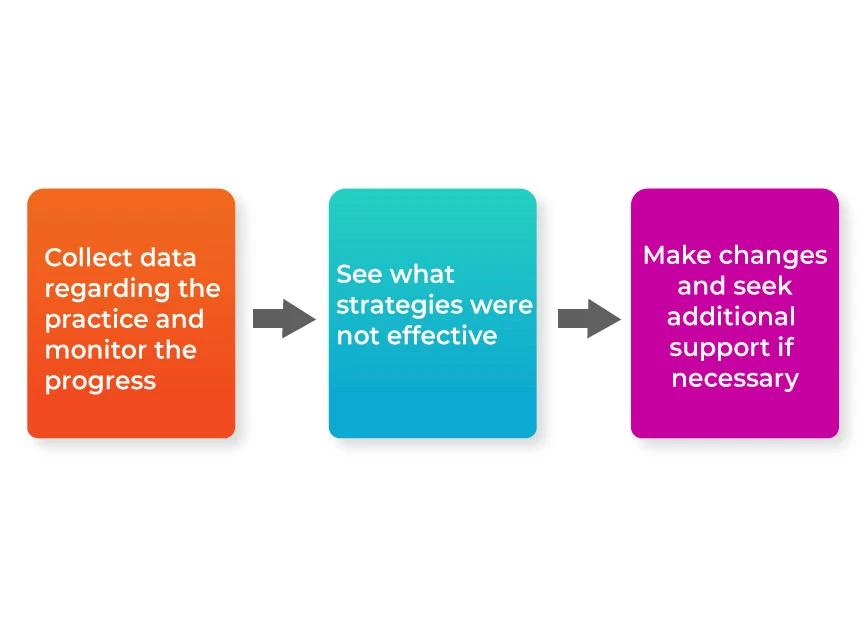
Monitoring and Evaluating Inclusion Strategies
It is important to ensure strict monitoring of the various inclusive strategies. Systematic and structured evaluation is essential for proper functioning of an inclusive education system. The following is a flow chart on how to monitor and evaluate the progress and effectiveness of inclusive strategies.
Inclusive education is flexible and supports all types of learners. For inclusion to be successful, teachers, parents, and other professionals must work together. It is necessary to ensure that all learners have access to the content by using different types of teaching methods. Adaptations should be implemented in a classroom for the children in need. Through inclusion, children become capable of participating in a group that would aid their development.

